Pipe bending technology is widely used in the creation of various piping systems.
Pipe bending is a critical process in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to construction and manufacturing. Whenever a project requires piping systems, exhaust assemblies, or custom metal components, the ability to bend pipe precisely and efficiently can make the difference between a successful outcome and a costly redesign. Because every application has different requirements for strength, durability, and accuracy, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, several pipe bending methods exist, each with its own advantages and limitations.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common pipe bending methods and help you determine which one might be best suited for your project.
1. Press Bending
Press bending is one of the simplest methods, where a die is pressed against the pipe to force it into shape. This approach is fast and economical, making it useful for projects that don’t require extreme precision. However, because it can cause deformation in the pipe’s cross-section, press bending is less ideal for applications where uniformity and smooth flow of fluids or gases are critical.
Best for: Low-cost, large-radius bends where minor distortion is acceptable.
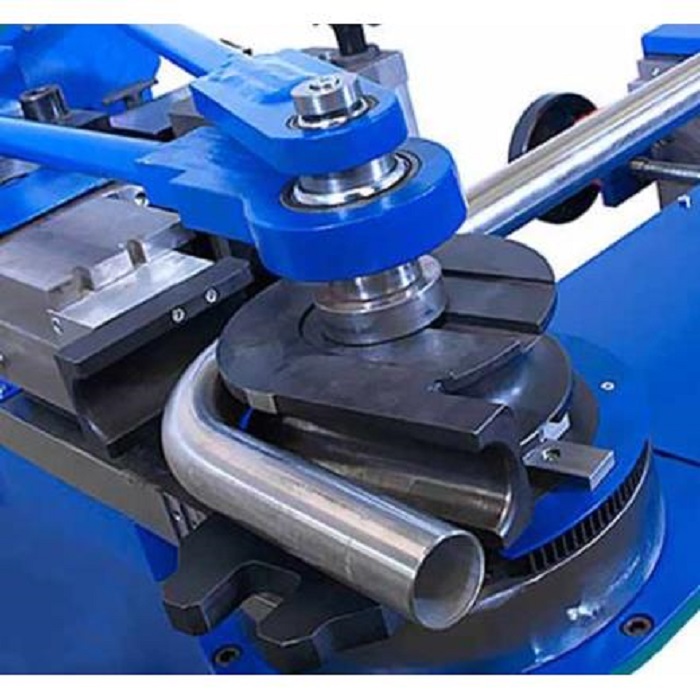
2. Rotary Draw Bending
Rotary draw bending is one of the most widely used techniques for precision work. In this method, the pipe is clamped onto a die and drawn around a fixed radius. The controlled process allows for tight bends with consistent dimensions, making it perfect for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries. This method also supports tooling customization, which is useful for complex designs.
Best for: Automotive exhaust systems, roll cages, and aerospace components.
3. Mandrel Bending
Mandrel bending builds upon rotary draw bending by inserting a mandrel (a solid rod or flexible ball assembly) into the pipe during the bending process. This prevents the pipe walls from collapsing or wrinkling, which is especially important when working with thin-walled tubing. The result is a clean, smooth bend that maintains the pipe’s structural integrity and flow efficiency.
Best for: Thin-walled pipes, tight-radius bends, and projects where maintaining internal diameter is critical.
4. Compression Bending
Compression bending involves clamping one end of the pipe and pushing the other end against a stationary die. This method is often used for bending electrical conduits, lightweight piping, or applications where aesthetics and precision are less critical. While effective for basic bends, it can lead to ovalization of the pipe’s shape under stress.
Best for: Electrical conduit systems, lightweight tubing, and simpler projects.
5. Roll Bending
For larger pipes or projects requiring gradual curves, roll bending is often the method of choice. This process uses a set of rollers to progressively curve the pipe into shape. Roll bending is ideal for projects that need sweeping arcs rather than sharp angles, such as architectural designs or structural supports.
Best for: Large-radius curves in construction, architectural elements, and heavy industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Pipe Bending Method
The decision often comes down to three factors: precision, budget, and application. For high-performance industries like automotive or aerospace, rotary draw or mandrel bending is usually preferred due to their accuracy. For more straightforward, cost-sensitive projects, press or compression bending may be sufficient. Roll bending, meanwhile, serves as the go-to option when working with larger diameters or creating aesthetic designs.
It’s also important to consider the material being bent. Aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel each respond differently under pressure, and choosing the correct bending method ensures that the material’s strength and durability are preserved.
Conclusion
Pipe bending is more than just shaping metal—it’s about ensuring that every bend meets the specific demands of the project. Whether it’s a precision automotive exhaust system, a structural support beam, or a simple conduit, selecting the right bending method can impact efficiency, durability, and overall performance. By understanding the various techniques available, businesses and engineers can make informed choices that lead to stronger and more reliable results.










Оставить коммент.