The United States boasts a diverse and multifaceted education system, catering to students from preschool through to university. This system, decentralized and influenced by local policies, offers various pathways depending on students’ academic interests and career goals. Here, we explore the different educational levels, including preschools, schools, colleges, and universities, and what each offers to the American student.
Preschool Education
Preschool, also known as pre-kindergarten or nursery school, serves as the initial step in the educational journey for children in the U.S. Typically catering to children aged three to five, these institutions focus on early childhood education. They aim to develop essential social, cognitive, and fine motor skills through play-based learning and structured activities. Though not mandatory, preschool is considered crucial for early development and prepares children for the rigors of formal schooling.
Elementary and Secondary Schools
Elementary school begins at kindergarten and usually continues until the fifth or sixth grade, depending on the state. Here, children are taught fundamental subjects such as English, Mathematics, Sciences, and Social Studies. The transition to middle school marks a shift to a more departmentalized approach where teachers specialize in subjects, guiding students through to high school.
High school, typically encompassing grades nine through twelve, prepares students for college, vocational training, or entering the workforce. It culminates in a diploma upon graduation and includes options for advanced placement courses and electives that cater to the student’s interests and career aspirations.
Higher Education: Colleges and Universities
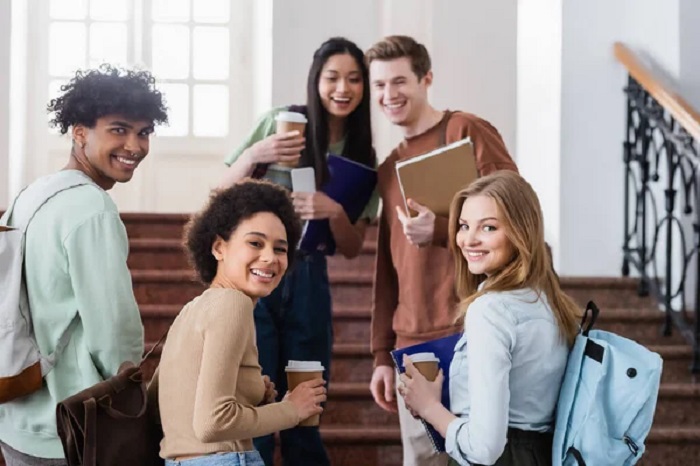
Higher education in the U.S. is renowned worldwide, offering a wide range of options from community colleges to prestigious universities. Community colleges primarily offer two-year associate degrees and certificates, serving as a stepping stone to four-year universities or as a pathway into various professions.
Universities and four-year colleges offer bachelor’s degrees and postgraduate programs, including master’s and doctoral degrees. These institutions are often research-oriented, providing opportunities not only for academic growth but also for professional development through internships and cooperative education programs.
Special Education and Alternative Schooling
The U.S. education system is also inclusive, providing comprehensive services for students with disabilities through the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). This act ensures students receive individualized education plans (IEP) in the public school system.
Additionally, alternative schooling options such as charter schools, magnet schools, and homeschooling allow parents and students to choose educational paths that best suit their individual needs. Charter schools operate with more flexibility than public schools, whereas magnet schools focus on specific disciplines like science, technology, or the arts.
Overview of Age, Duration, and Institution Types in the U.S. Education System
| ducation Level | Age Range | Duration of Study | Type of Institution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preschool | 3-5 years | 1-3 years | Nursery, Preschool, Pre-Kindergarten |
| Elementary School | 5-10/11 years | 5-6 years | Elementary School |
| Middle School | 11-13/14 years | 2-3 years | Middle School, Junior High School |
| High School | 14-18 years | 4 years | High School |
| Community College | 18+ years | 2 years | Community College |
| Undergraduate College/University | 18+ years | 4 years | College, University |
| Graduate School | 22+ years | 2-6 years | Graduate School, University |
The educational structure in the U.S. is designed to provide multiple pathways for students, accommodating a range of abilities and interests. From the foundational years in preschool to the expansive opportunities in higher education, the system is equipped to support lifelong learning and success. Understanding the intricacies of this system can help students and parents make informed decisions that align with their educational and career goals.










Оставить коммент.